Comprehensive orthodontics
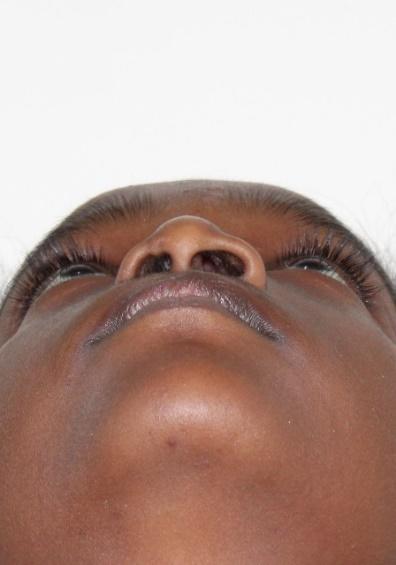
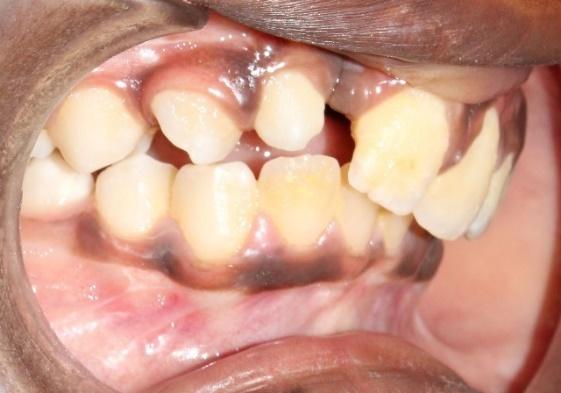
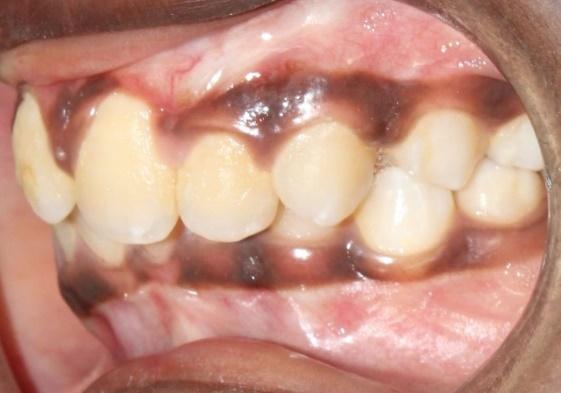
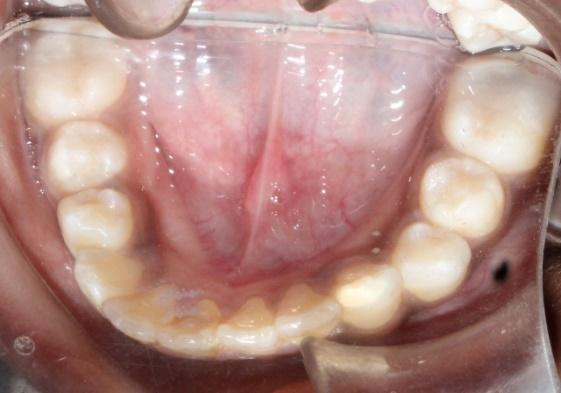
The malocclusions observed in individuals with clefts present peculiar complexities that differentiate them from occlusal irregularities of individuals without clefts. Comprehensive orthodontic treatment of patients without or with mild midfacial deficiency is initiated when the permanent dentition is completed.
The planning for the comprehensive orthodontic treatment should include intra-arch and inter-arch objectives. The intra-arch therapeutic options include:
1) Maintenance of the maxillary lateral incisor in the cleft area when it is present and show a good root length;
2) Space closure of the region of missing maxillary lateral incisor by orthodontic mesialization of posterior teeth at the cleft side;
3) Space maintenance of the missing lateral incisor for implant placement after completion of orthodontic treatment;
4) Implant placement at the canine-premolar region after moving the maxillary canine toward mesial at the space of the absent lateral incisor.
There are two inter-arch therapeutic options for patients with Class III skeletal pattern. The selection will depend on the GOSLON index as well as on the facial esthetics.
1) Compensatory orthodontic treatment: indicated for individuals with occlusal scores Goslon 3 and acceptable facial esthetics, since the orthodontic treatment alone does not improve the facial appearance. Mandibular extractions may be necessary in this therapeutic option.
2) Decompensation orthodontic treatment for orthognathic surgery
Treatment Plan
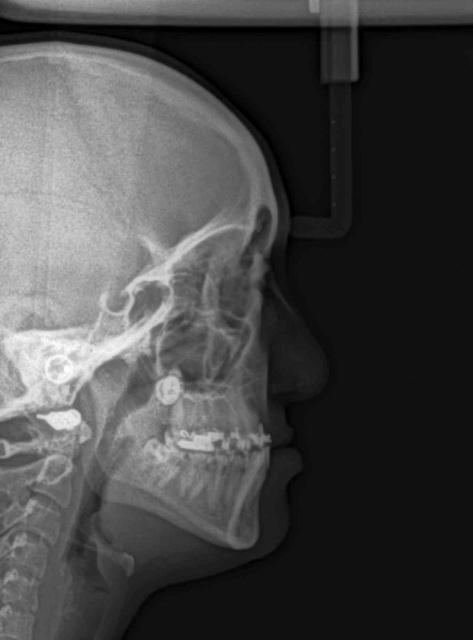
2D lateral cephalogram
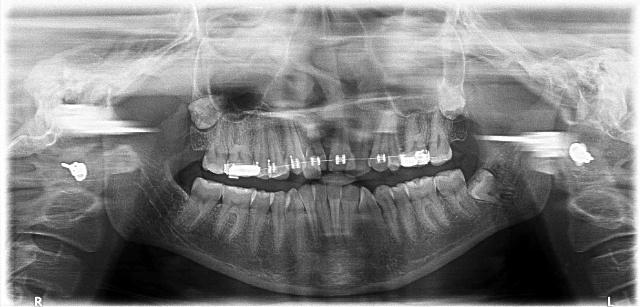
2D orthopantomography
Intraoral scan
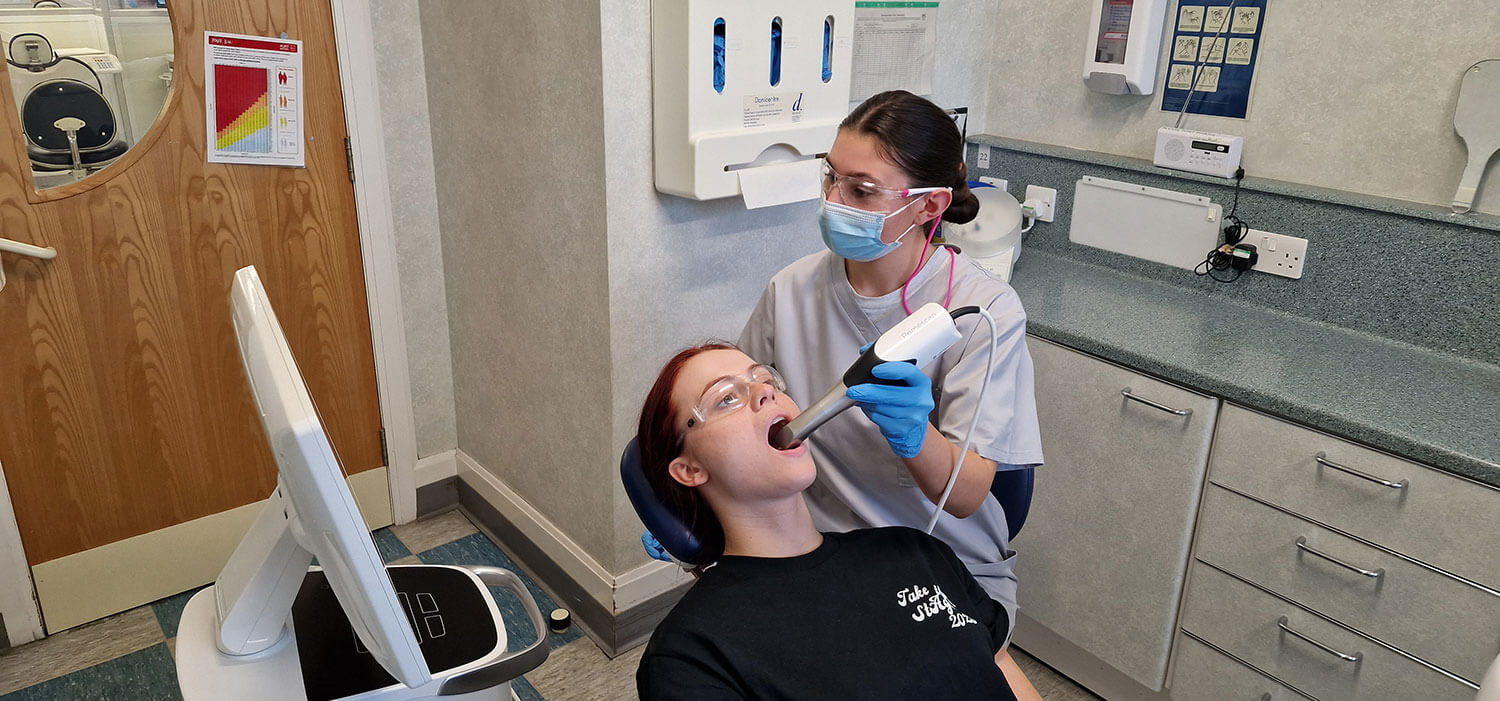
Appliance design/manufacturing
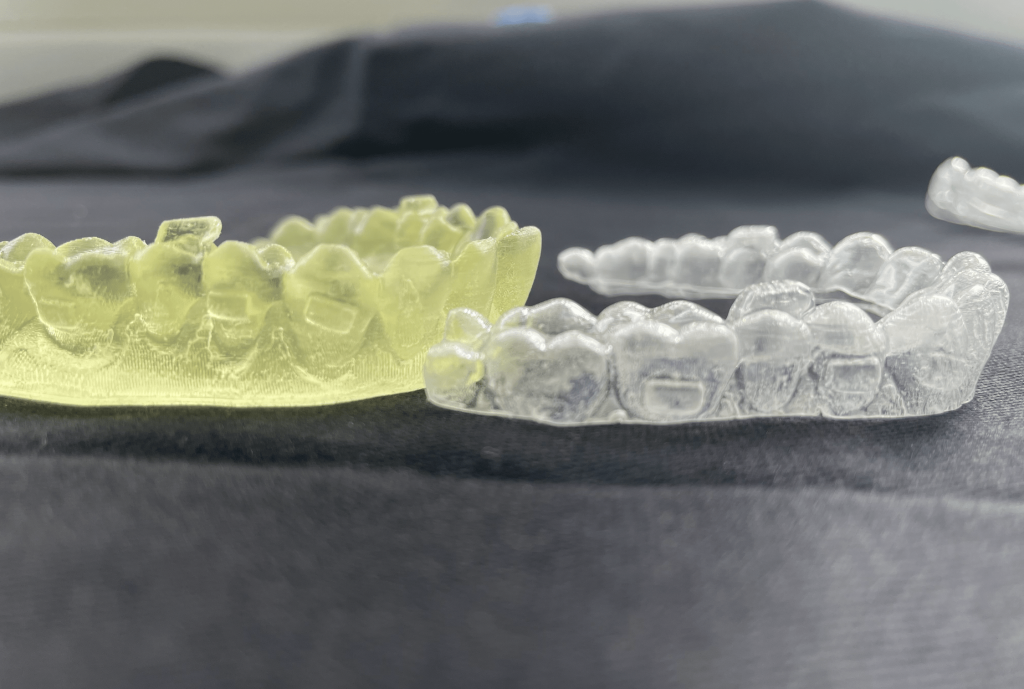

Appliance delivery
Remote monitoring
What is remote monitoring?
It is the use of digital technologies to monitor and capture medical and other health data from patients and electronically transmit this information to healthcare providers
Ways of remote monitoring?
Devices that track heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, sleep quality, etc. These are collected from the patient’s location, then analyzed, interpreted, and transmitted to the caretaker at another location.

 Our use of cookies
Our use of cookies 





















 Previous
Previous 
